STING
-
STING识别cGAMP(cyclic dinucleotide guanosine monophosphate-adenine monophosphate),诱导IFN依赖抗病毒免疫。 -
STING识别细菌CDNs(cyclic dinucleotides), 诱导抗细菌免疫。 -
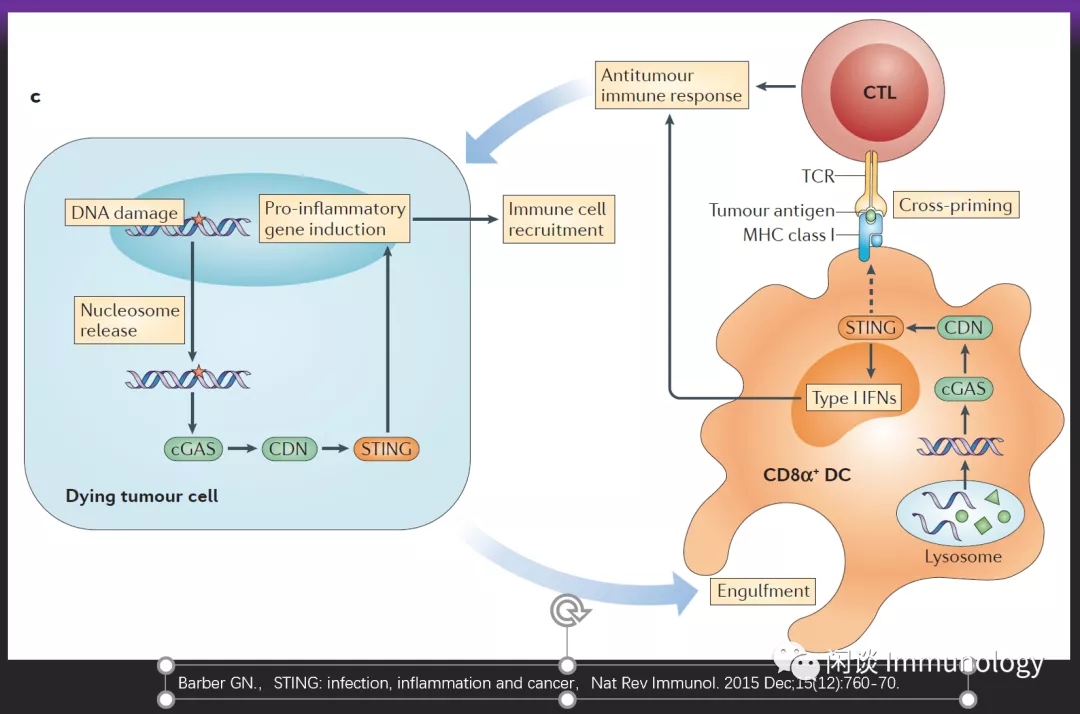
肿瘤裂解产生的DNA激活cGAS,裂解DNA产生cGAMPs。cGAMPs被APC细胞和T细胞中的STING识别,诱导IFN依赖的抗肿瘤免疫。
STING抗感染免疫
-
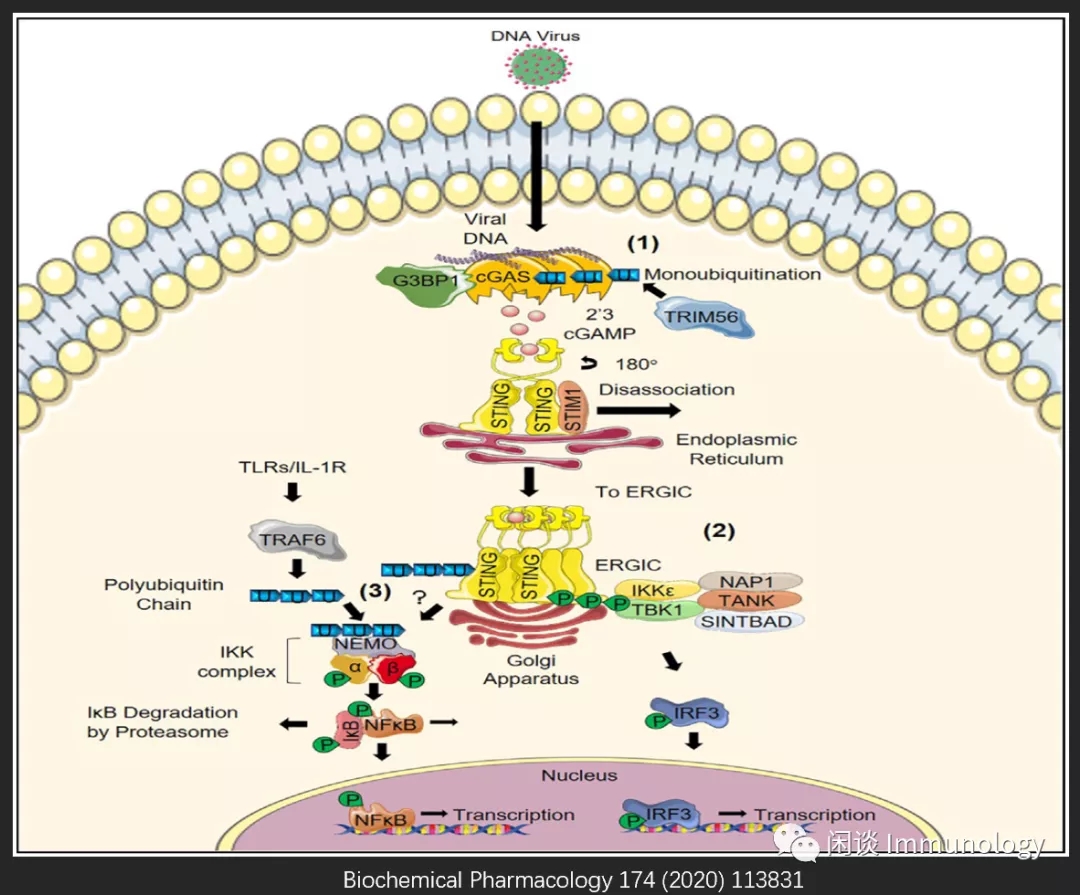
胞质DNA传感器cGAS与病毒DNA结合,并被TRIM56泛素化。G3BP1与cGAS相互作用,形成大的cGAS复合物。c GAS催化ATP和GTP,转化为2‘3cGAMP(一个循环的第二信使),与STING二聚体形成的配体结合结构域结合。结合结构域发生180°旋转,STING被激活。E3连接酶(如TRAF6或TRIM32),多泛素化组件与STING形成复合物。
-
激活的STING从STM1解离,从内质网进入高尔基体,与TBK1作用,使IRF3磷酸化。磷酸化IRF3进入核内,激活转录因子,IFN表达。
-
STING激活NF-κB的确切机制还不是特别清楚。可能与TLR/IL-1R通路相关,引起IKK磷酸化,进而引起NF-κB磷酸化,入核,引起转录激活。
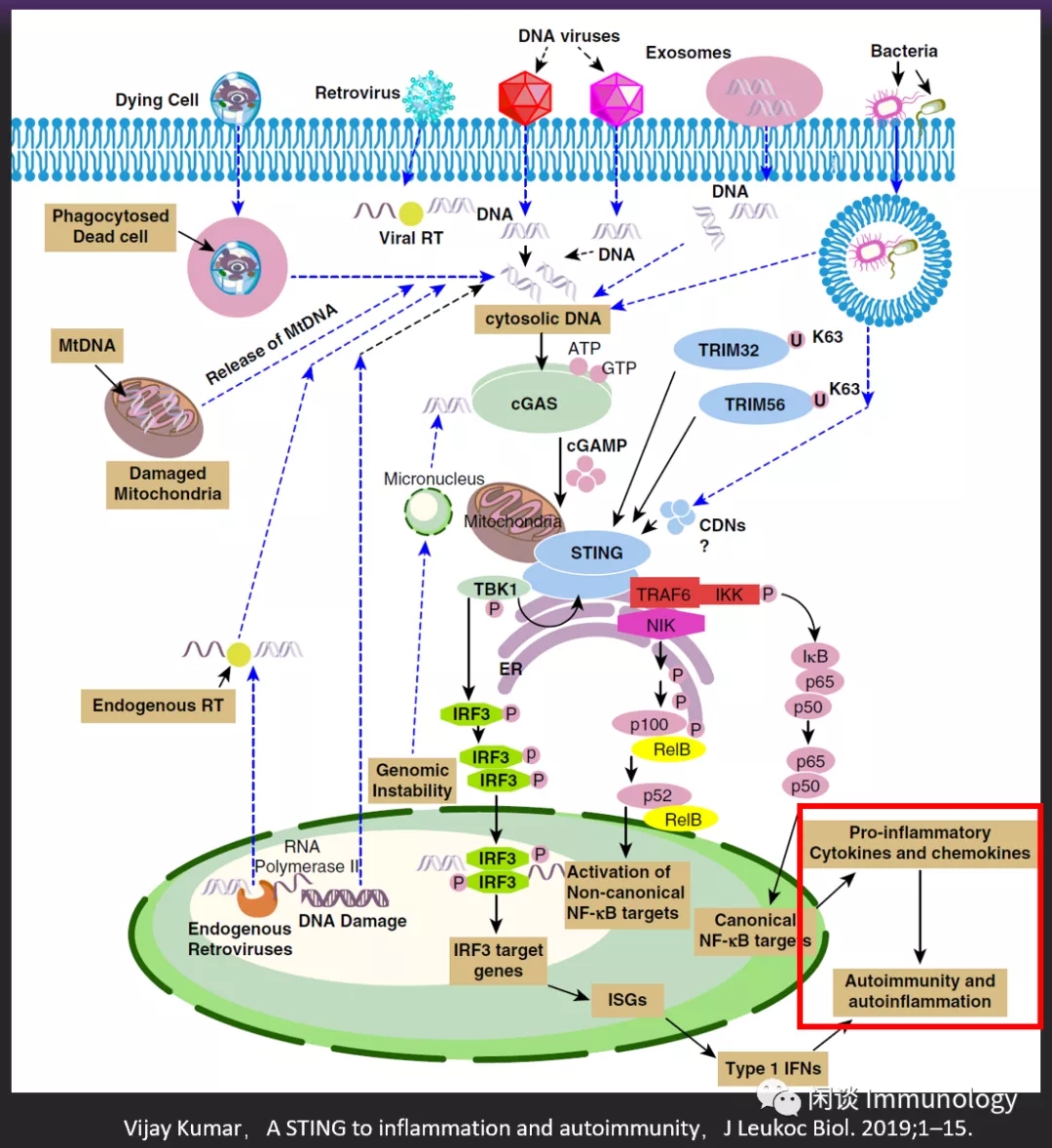
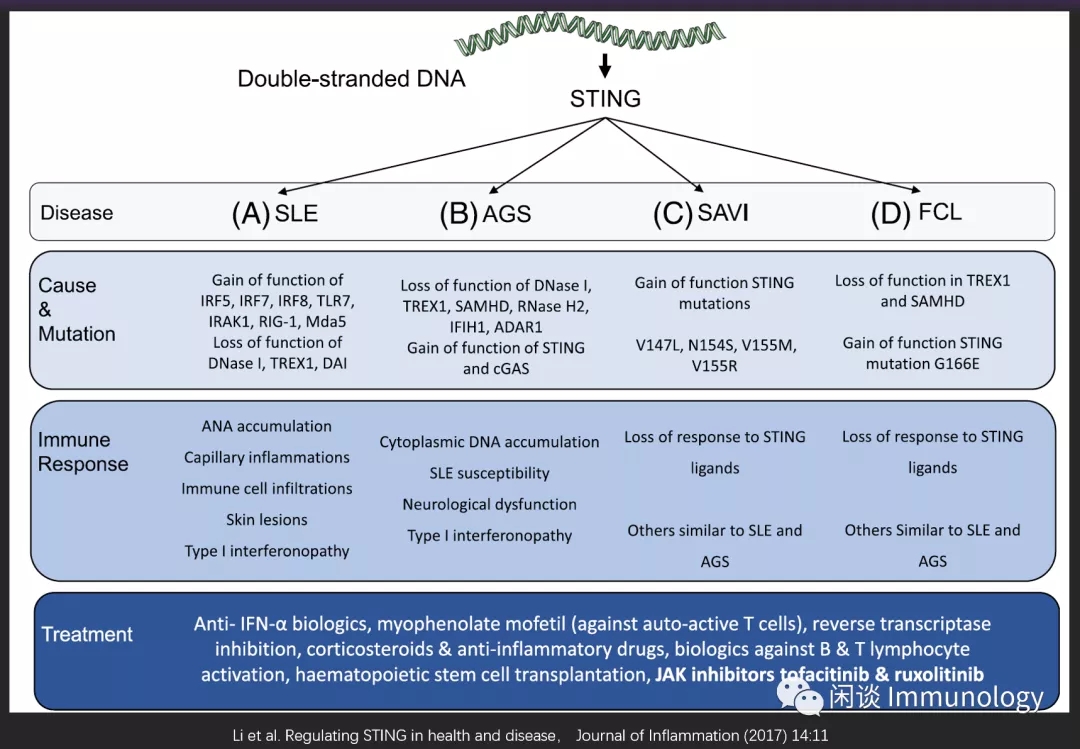
自身DNA释放,激活STING,引起SLE等自身免疫性疾病。
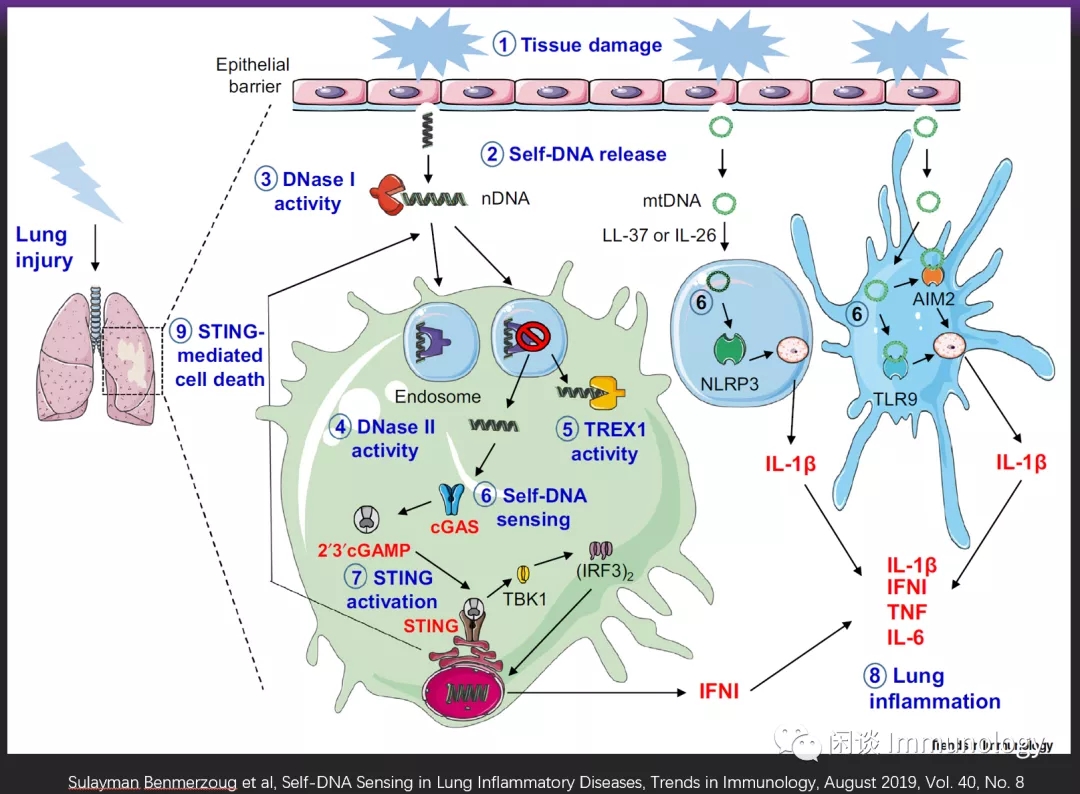
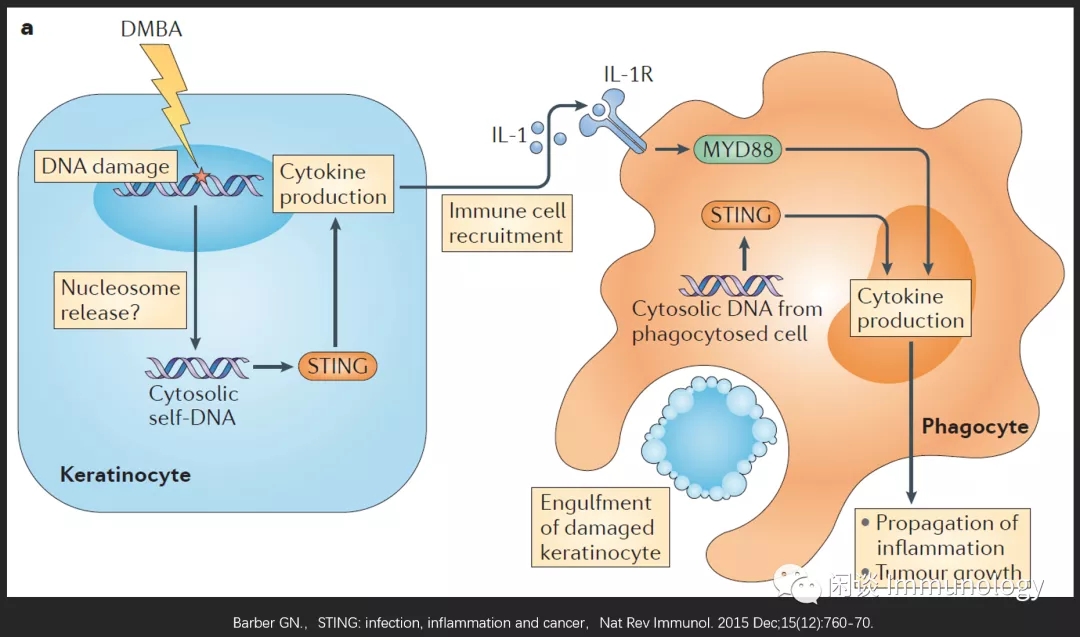
肺部感染,PM2.5,其他污染物,衰老等,引起上皮细胞损伤,释放DNA,被免疫细胞吞噬,活化STING,进而引起促炎症因子释放。损伤细胞释放DNA被APC吞噬后,也可以引起炎症小体组装,IL-1β产生,进而加重炎症。
感染性肺炎,老年衰老引起肺炎等,甚至COVID-19,可能都有关。
STING与肿瘤
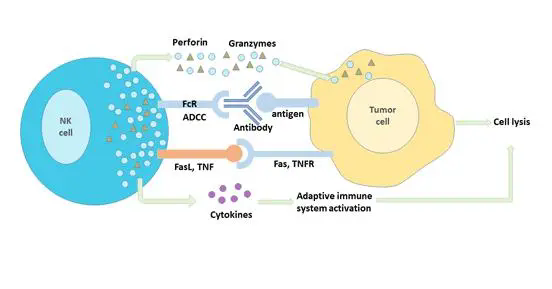
STING依赖性抗肿瘤细胞毒性T淋巴细胞(CTL)
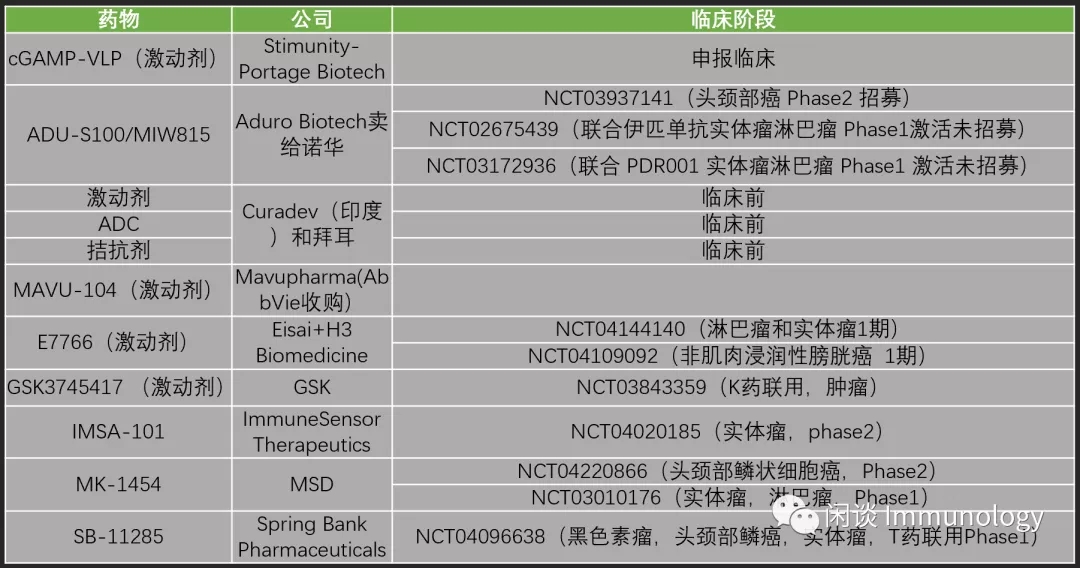
在免疫检查点抑制剂抗肿瘤治疗中,STING信号具有关键作用(文献6,7)。多个STING激动剂(比如cGAMP)和免疫检查点抑制剂(K药,T药,伊匹单抗等)联合使用,在进行实体瘤,淋巴瘤,头颈部鳞癌临床研究。
STING药物开发概况
主要参考文献
-
Ishikawa, H. and Barber, G.N. (2008) STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 455, 674–678
-
T. Phelan, et al. Targeting of the cGAS-STING system by DNA viruses,Biochemical Pharmacology 174 (2020) 113831
-
Cerboni, S. et al. (2017) Intrinsic antiproliferative activity of the innate sensor STING in T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 214, 1769–1785
-
Vijay Kumar,A STING to inflammation and autoimmunity,J Leukoc Biol. 2019;1–15. -
Barber GN.,STING: infection, inflammation and cancer,Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Dec;15(12):760-70. -
Deng, L. et al. (2014) STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing promotes radiation-induced type I interferon-dependent antitumor immunity in immunogenic tumors. Immunity 41, 843–852 -
Wang, H. et al. (2017) cGAS is essential for the antitumor effect of immune checkpoint blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114, 1637–1642 -
Li et al.Regulating STING in health and disease, Journal of Inflammation (2017) 14:11 -
Sulayman Benmerzoug et al,Self-DNA Sensing in Lung Inflammatory DiseasesTrends in Immunology, August 2019, Vol. 40, No. 8
扫描上面二维码在移动端打开阅读