(图片摘自www.sciencealert.com)
癌症的治疗是目前医学领域备受关注的领域之一,美国目前有将近1450万人患有癌症,同时每年又有1300万新增病例出现。人工智能的出现为癌症的治疗提供了新的生机。来自密歇根大学的研究者们运用了一种新的方法能够消除患者体内的肿瘤。
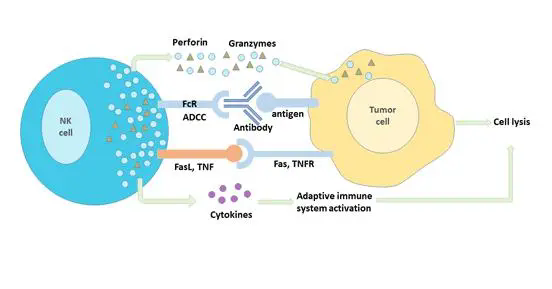
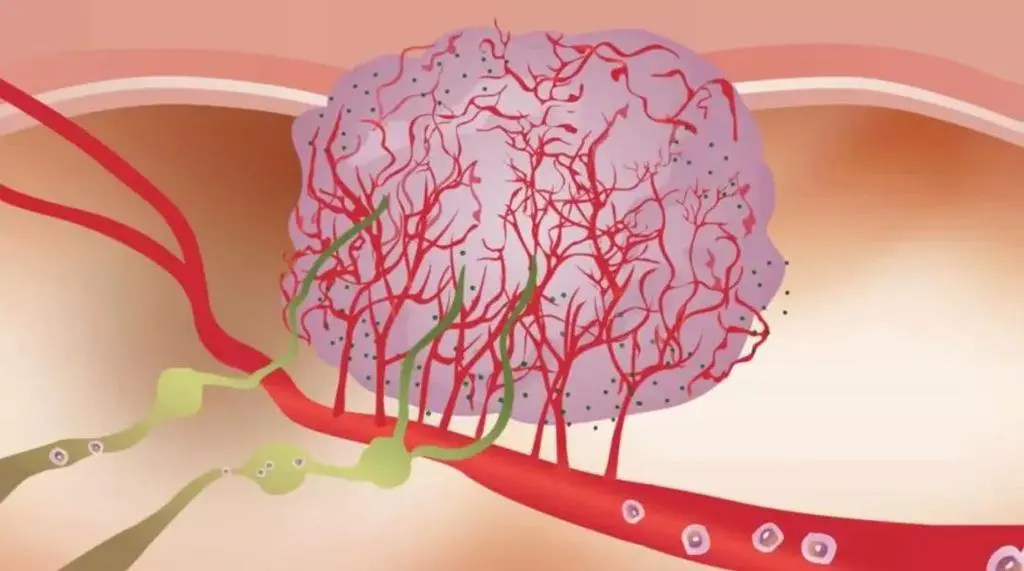
这一新型的技术是通过利用大小约为10nm的微型芯片,从而诱导机体杀伤肿瘤细胞。
“我们的目的是利用这些小型的芯片教育免疫系统,让其识别体内的肿瘤细胞并进行杀伤”,该研究的首席作者,来自密歇根大学的James Moon说道。
这些小芯片上装载着肿瘤特异性的抗原标记,进而导致特异性识别肿瘤抗原的免疫细胞分化与激活。
这一新型的疗法与已有的免疫检查点疗法药物联合使用,能够有效地清除体内的肿瘤并防止其进一步的发生。
到目前为止,该药物已经在小鼠水平得到了验证:10天之内能够完全清除肿瘤。70天后再次给小鼠接种相同的肿瘤也能够有效地清除。这说明小鼠在接受治疗之后能够形成长期的免疫记忆。
当然,在该药物成功进入临床以前,我们还有很长一段路需要走。研究者们仍需要在大型动物水平进行进一步的验证,并最终进行临床试验。尽管如此,微芯片技术仍然提高了我们治疗癌症的几率。
相关结果发表在最近一期的《nature material》杂志上。(生物谷Bioon.com)
原始出处:Researchers are developing nanodiscs that can wipe out tumours
PMC:
PMID:
doi:10.1038/nmat4822
Designer vaccine nanodiscs for personalizedcancer immunotherapy
Rui Kuai, Lukasz J. Ochyl, Keith S. Bahjat,Anna Schwendeman & James J. Moon
Despite the tremendous potential ofpeptide-based cancer vaccines, their efficacy has been limited in humans.Recent innovations in tumour exome sequencing have signalled the new era ofpersonalized immunotherapy with patient-specific neoantigens, but a generalmethodology for stimulating strong CD8α+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responsesremains lacking. Here we demonstrate that high-density lipoprotein-mimickingnanodiscs coupled with antigen (Ag) peptides and adjuvants can markedly improveAg/adjuvant co-delivery to lymphoid organs and sustain Ag presentation ondendritic cells. Strikingly, nanodiscs elicited up to 47-fold greaterfrequencies of neoantigen-specific CTLs than soluble vaccines and even 31-foldgreater than perhaps the strongest adjuvant in clinical trials (that is, CpG inMontanide). Moreover, multi-epitope vaccination generated broad-spectrum T-cellresponses that potently inhibited tumour growth. Nanodiscs eliminatedestablished MC-38 and B16F10 tumours when combined with anti-PD-1 andanti-CTLA-4 therapy. These findings represent a new powerful approach forcancer immunotherapy and suggest a general strategy for personalizednanomedicine.
扫描上面二维码在移动端打开阅读